
Wireless charging was all the rage in smartphones a few years ago, but most device makers have backed off on the technology. Many phones simply charge super-fast via a cable now. The fatigue is due in part to the range limitation of the technology. True wireless power is still a no-go in consumer technology, but Disney Research has developed a version that might work in the future. Its volumetric wireless power system can keep hundreds of devices powered with no wires whatsoever. The main drawback: . The range of current wireless charging standards is a few inches at best, which means you can only juice up a device in a limited area — you essentially have to set it down on a charging pad.

For months, computer enthusiasts have chafed for fresh official information on Ryzen, as opposed to the stream of unverified leaks. Today, AMD is releasing detailed product information, pricing, and estimated IPC improvements over Excavator. Hold on to your hats, ladies and gentlemen — things are about to get real interesting in the PC market. For those of you just tuning in, is AMD’s last, best chance to prove it can compete effectively against Intel’s Core i3/i5/i7 product lines. For years, AMD has been stuck trying to compete against Intel’s top-end chips with its Piledriver-based architecture. Ryzen is a new architecture, completely unrelated to AMD’s previous Bulldozer / Piledriver / Steamroller / Excavator product lines.
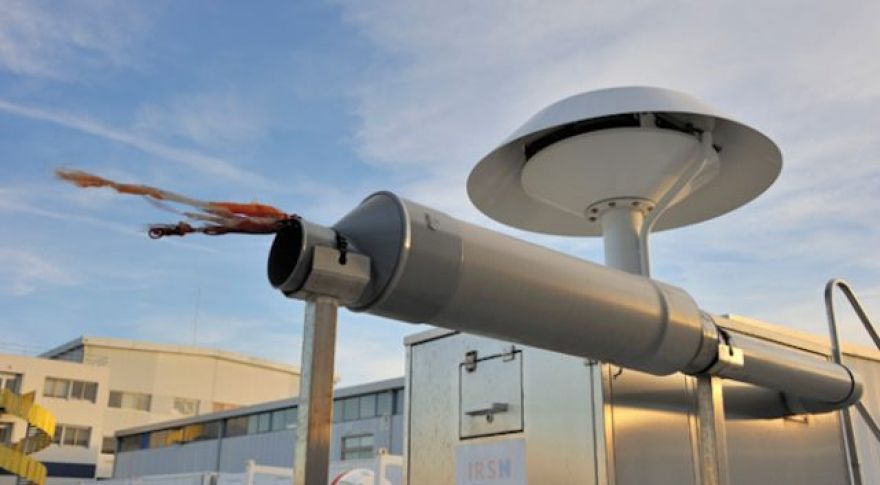

France’s public institute for radiological and nuclear risks (IRSN) they detected tiny amounts of iodine-131, a radionuclide of human origin, in the “ground-level atmosphere” all across Europe back. The isotope was in the second week of January over northern Norway, after which it moved over Finland, Poland, Germany, the Czech Republic, France, and Spain. Levels have already returned to normal. “Since only Iodine-131 was measured, and no other radioactive substances, we think it originates from a pharmaceutical company producing radioactive drugs. Iodine-131 is used for treatment of cancer,”Astrid Liland, head of the section for emergency preparedness at their NRPA, Motherboard,

Ready to replace your aging PC with something new? Dell is currently offering up a 42% discount on the XPS 8900 desktop. With a quad-core Skylake CPU, lots of speedy DDR4 memory, and plenty of room for expansion, you’ll be hard-pressed to find a better tower with a price this low. (List price: $1045.85 — Coupon code: XPS599) In terms of specs, the XPS 8900 is rocking a sixth generation quad-core 3.4GHz Intel Core i7-6700 processor, 8GB of DDR4 RAM (2133MHz), a discrete Nvidia GeForce GT 730 graphics card (with 2GB of memory), a 1TB 7200RPM hard drive, a DVD drive, Bluetooth 4.0, and 802.11b/g/n/ac WiFi support.
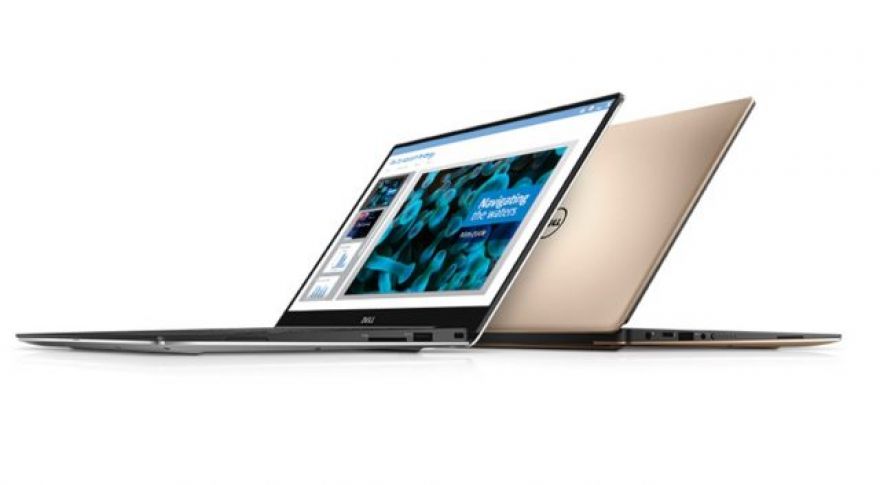

After the rise of the MacBook Air, similar Windows-based laptops have seen widespread success, and it’s easy to understand why. With a slim form factor and a focus on flexibility, these highly portable laptops are excellent fits for most consumers. Unfortunately, they tend to be on the pricey side, but we’ve just found a superb bargain from Dell. With the use of today’s coupon code, you can save a total of $300 on a Dell XPS 13. • (List price: $1349.99 — Coupon code: XPS1049) • (List price: $1099.99 — Coupon code: TENOFF) On the inside, this laptop features a seventh generation dual-core 2.7GHz Intel Core i7-7500U CPU, integrated Intel HD Graphics 620, 8GB of LPDDR3 RAM (1866MHz), a 256GB solid-state drive, Bluetooth 4.1, and 802.11b/g/n/ac WiFi support.
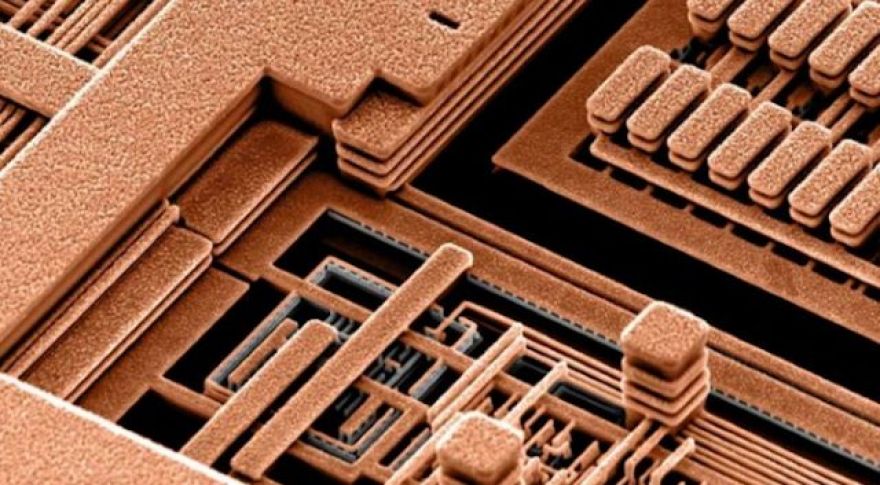
Most of the time, when we talk about the potential impact of next-generation technologies on future computers, we’re talking about transistor performance. This makes sense — transistor scaling is what covers, and improving transistor density and design is what drove the “better, faster, cheaper,” mantra for nearly 40 years. But transistors aren’t the only area of CPU design that could benefit from dramatic improvements to underlying technology — and a at Stanford believes it can address another critical problem that’s holding modern chips back, by building connective structures via copper and graphene combined rather than just copper. Every modern CPU is wired together via an extensive network of copper wires, dubbed “interconnects.
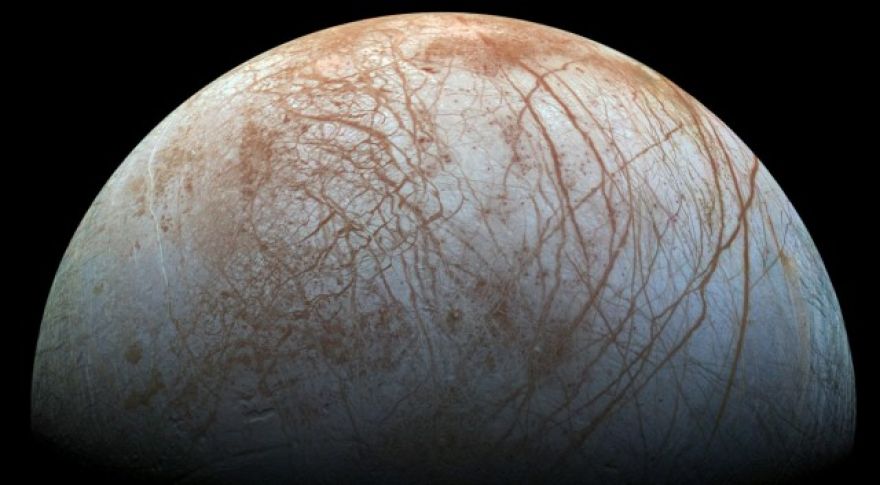

India by sending 104 satellites into space in a single launch. One hundred and three of them were nanosats, but they were crated beside Cartosat-2D: a three-quarter-ton beast the Indian government is going to use for cartography, imaging and maybe weather mapping. Ninety-six of the 103 were actually American spacecraft from a company called Planet, which was founded by ex-NASA scientists to “image the entire Earth every day.” Counting the 96 new ones, that brings Planet’s constellation to 149, which is also a world record. The latest news on is that scientists have revised the odds on its habitability, probably downward.
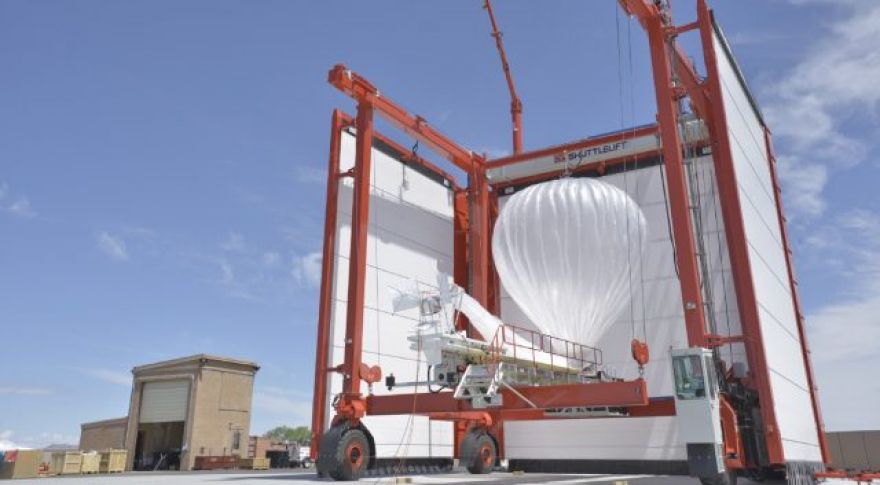

The aptly named Project Loon in 2011. The goal was to provide wireless internet access to remote areas with high-altitude balloons, which does indeed sound loony. It has become one of the most well-known endeavors by X, now a division of Google’s parent company Alphabet. It’s not just a wacky idea anymore — . X has announced improvements to its navigation algorithm that could vastly reduce the number of balloons needed to cover an area. Early experiments in were basically designed to prove it wouldn’t work. Was it even possible for these balloons to cover large distances? Could they navigate on air currents? Could they be steered to specific locations? The answer to all those questions turned out to be an emphatic and surprising “yes.

Early results say US traffic fatalities increased by 3% to as much as 6% in 2016 over 2015. Texting and other smartphone apps are cited frequently by safety officials for the increase. They’re also pointing to the usual suspects, too: seat belts not worn, seat belt laws not enforced, speeding, drunken driving, and legislators unwilling to pass more safe-driving laws. The size of the increase depends a lot on how you define the numbers. In raw data, National Safety Council data shows an increase of 6% in 2016 over 2015. But if you factor for the growing population and/or the number of miles driven, it’s 3%.









